By Luke Smith · 2/23/2016

At datacenterHawk, we've recently reviewed how cloud computing, gaming, healthcare, and social media are driving growth in the data center market. One other industry that generates data center demand is mobile app development. With approximately 200 million smartphone users and 82 million tablet users in the United States, the development and use of mobile apps is steadily increasing. The choices for smartphone and tablet users are endless, as Google Play has over 1.6 million apps and the Apple App Store offers over 1.5 million apps. Companies creating these applications are continually searching for the best ways to manage the infrastructure and data associated with their app development. In this blog, we'll discuss how these apps consume data, and its impact on the data center industry.
Whether it's a streaming service, social media app, web browser, or game, all apps use data. The average smartphone user consumes approximately 2.5 GB of mobile data, and over 10 GB of Wi-Fi data per month in the United States. If every one of the 200 million smartphone users used 2.5 GB per month, 500 petabytes (500 million gigabytes) of mobile data would be consumed monthly in the United States, and six exabytes (6 billion gigabytes) of data every year. In the above scenario, it would take one person using 2.5 GB per month over 16 million years to use the amount of data consumed in the United States per month. According to the Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile Data Traffic Forecast, global mobile data traffic is over 3.7 exabytes per month.
The amount of data traffic comes from several different sources:
Types of Apps – Not every app uses data the same. For example, playing a mobile game uses less data than streaming services like Spotify or Netflix. On the highest streaming setting, it takes roughly seven hours to stream 1 GB of music on Spotify. AT&T reported 164 TB of utilized mobile data traffic during Mardi Gras this year, mostly from social media apps. Navigational apps, like Apple or Google Maps, require a constant connection to provide the user with up-to-date directional information. Other apps, like e-reader apps, require data to download the e-book. Although messaging apps, iMessage for example, use small amounts of data per message, they process massive quantities of messages. In 2014, Apple CEO Tim Cook reported Apple handled approximately 40 billion iMessages per day from users communicating through the iCloud.
Number of App Users – Although there are millions of downloadable apps, most of them are unused. According to the Nielsen Company, the majority of data generated by mobile apps comes from a few specific programs. As an example, Facebook averages 126.7 million unique mobile visitors, YouTube averages 97.6 million average visitors, and Google Maps averages 87.7 million visitors per month. Also, most of the heavily used apps are also high data using apps.

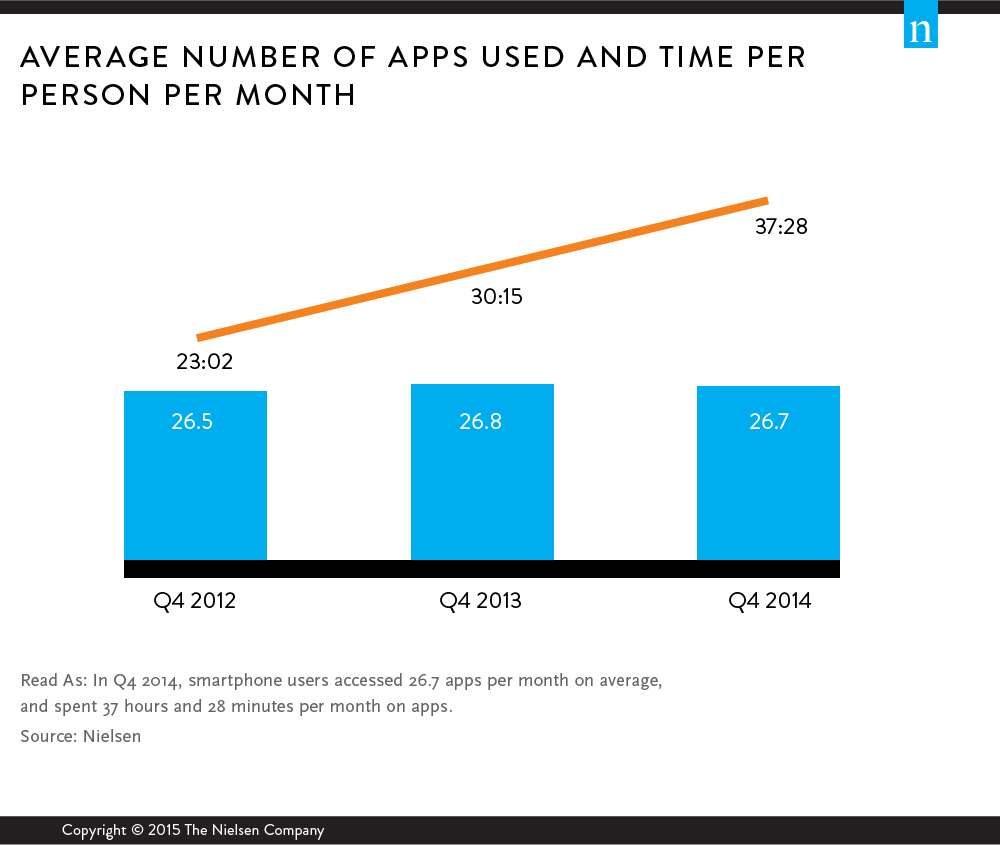
Time Spent On Apps – While different apps use varying amounts of data, much of the data usage is related to time spent on those programs. Accessing a high data using app for a short time is similar to accessing a low data using app for a long time. Another study by the Nielsen Company shows that while people use only 26-27 apps on average, they spend approximately 37 hours per month on those apps. Trends today reveal while the number of apps the average person uses per month is remaining the same, the amount of time spent on them is increasing. As people commit more of their time to these programs, data usage will increase.
Data center solutions for companies creating apps is challenging, and a well crafted strategy is important for success. Usage and traffic can change quickly, creating scalability needs. Some apps cost money or have in-app purchases, requiring a higher level of data security. Many companies producing mobile apps utilize cloud services to meet these needs, and many cloud companies now offer app platforms in their available services. The Cloud makes it easy to scale to the load generated by app users. Since apps generally require a small amount of infrastructure, the cloud offers a platform that the can manage the maintenance of the app without the owner having to buy, house, and manage their own infrastructure.
The usage of mobile devices is continually expected to increase in the future. Cisco predicts global mobile data traffic will exceed 30.6 exabytes per month, and the number of mobile-connected devices per capita will reach 1.5 by 2020. Data center companies will have to continue to expand, and strengthen their services in order to meet this rising need.